- Install Putty On Mac Catalina Free
- Install Putty On Mac Catalina Os
- Install Putty On Mac Catalina Download
We already have a tutorial on how to install macOS Catalina on Linux. A simple tutorial on how set up a macOS VM in QEMU, accelerated by KVM. This is basically the same tutorial but everything runs, near native with X11 forwarding, in Docker.
The Suzuki GSXR of terminals. Or your ditzy, blonde high school cheerleader; fast and pretty but not a lot going on under the hood. Eschews a negative developmental philosophy towards including said functionality, with the official reason cited in project documentation as 'Not within the realm of a terminal emulator' and ostensibly, 'best left up to other tools such as terminal multiplexers. Ported PuTTY for Mac. Mac has the port of PuTTY which can be installed in various ways described as below: Installation using Homebrew: Use the below-given command to install PuTTY in case you have already installed “brew”command.sudo brew install putty; Installation using MacPorts: PuTTY is easily available through MacPorts. Please find the steps belowInstall XcodeInstall Command Line Tools From Apple AccountDownload and install XQuartzDownload and install MacPorts.sudo port -v. Download and install the OS X Smartcard Services package The OS X Smartcard Services Package allows a Mac to read and communicate with a smart card. In order for your machine to recognize your CAC certificates and DoD websites as trusted, the installer will load the DoD CA certificates on OS X. Download macOS Catalina from the Mac App Store Direct Link. Once the download is complete, close the installer window by selecting the Quit Install macOS option in the menu bar or using the.
This is not a Docker tutorial, but let’s have a quick look at how to install it on Arch linux ( more info for Docker on Arch here ). For other distros as well as how to install Docker on macOS and Windows, check out the official installation guide here.
- ALSO READHOW TO: Dual Boot macOS and Linux
- ALSO READHOW TO: Install macOS Big Sur With OpenCore on Linux
1. Open up the terminal and type sudo pacman -S docker
2. Once Docker is installed type in sudo systemctl start docker and sudo systemctl enable docker
3. By default only a user with root or sudo privilages can run or manage Docker. If you want to run Docker without root or having to add sudo every single time type sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
4. Reboot your machine
Install macOS in a Docker container
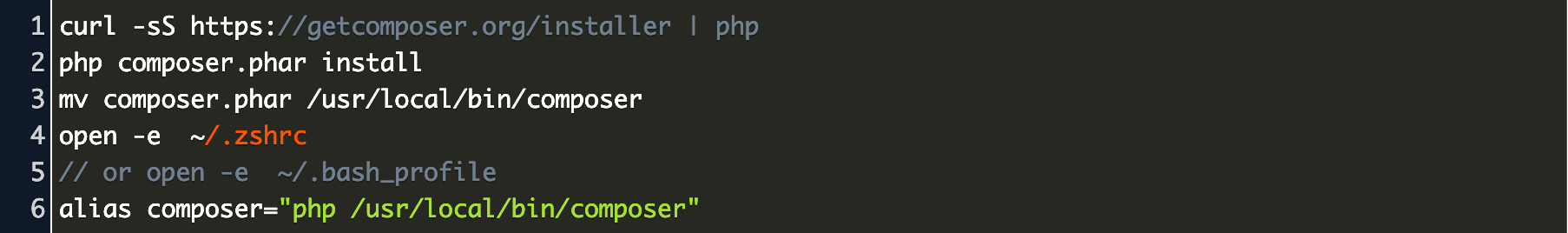
1. Make sure you have hardware virtualization turned on in BIOS
2. Install QEMU and requirements on the machine. Open up a terminal and type:
- Arch:
sudo pacman -S qemu libvirt dnsmasq virt-manager bridge-utils flex bison ebtables edk2-ovmf - Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt install qemu qemu-kvm libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon-system bridge-utils virt-manager - CentOS/Rhel/Fedora:
sudo yum install libvirt qemu-kvm -y

3. Now, run:sudo systemctl enable libvirtd.servicesudo systemctl enable virtlogd.servicesudo modprobe kvm
4. Reboot your machine
5. Now pull the image with docker pull sickcodes/docker-osx
6. Run docker run --privileged -e 'DISPLAY=${DISPLAY:-:0.0}' -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix sickcodes/docker-osx
7. Boot from macOS Base System
Install Putty On Mac Catalina Free
8. Now the macOS installer will load. Select Disk Utility and format the largest disk in the list.
9. Exit Disk Utility and and select Reinstall macOS
10. On restart, select macOS to continue the installation.
11. When the installation is finished, upon reboot select macOS to boot into macOS Catalina
12. That’s it finish setting up macOS Catalina and enjoy running macOS in a Docker container on your Linux machine.
To troubleshoot the installation as well as learn how to customize the build ( more RAM, more/less disk space, macOS version etc ) check out the project page here.
Quickstart
- Install Xcode and the Xcode Command Line Tools
- Agree to Xcode license in Terminal:
sudo xcodebuild -license - Install MacPorts for your version of the Mac operating system:
Installing MacPorts
MacPorts version 2.7.1 is available in various formats for download and installation (note, if you are upgrading to a new major release of macOS, see the migration info page):
- “pkg” installers for Big Sur, Catalina, and Mojave, for use with the macOS Installer. This is the simplest installation procedure that most users should follow after meeting the requirements listed below. Installers for legacy platforms High Sierra, Sierra, El Capitan, Yosemite, Mavericks, Mountain Lion, Lion, Snow Leopard, Leopard and Tiger are also available.
- In source form as either a tar.bz2 package or a tar.gz one for manual compilation, if you intend to customize your installation in any way.
- Git clone of the unpackaged sources, if you wish to follow MacPorts development.
- The selfupdate target of the port(1) command, for users who already have MacPorts installed and wish to upgrade to a newer release.
Checksums for our packaged downloads are contained in the corresponding checksums file.

The public key to verify the detached GPG signatures can be found under the attachments section on jmr's wiki page. (Direct Link).
Please note that in order to install and run MacPorts on macOS, your system must have installations of the following components:
Apple's Xcode Developer Tools (version 12.2 or later for Big Sur, 11.3 or later for Catalina, 10.0 or later for Mojave, 9.0 or later for High Sierra, 8.0 or later for Sierra, 7.0 or later for El Capitan, 6.1 or later for Yosemite, 5.0.1 or later for Mavericks, 4.4 or later for Mountain Lion, 4.1 or later for Lion, 3.2 or later for Snow Leopard, or 3.1 or later for Leopard), found at the Apple Developer site, on your Mac operating system installation CDs/DVD, or in the Mac App Store. Using the latest available version that will run on your OS is highly recommended, except for Snow Leopard where the last free version, 3.2.6, is recommended.
With Xcode 4 and later, users need to accept the Xcode EULA by either launching Xcode or running:
Apple's Command Line Developer Tools, which can be installed on recent OS versions by running this command in the Terminal:
Older versions are found at the Apple Developer site, or they can be installed from within Xcode back to version 4. Users of Xcode 3 or earlier can install them by ensuring that the appropriate option(s) are selected at the time of Xcode's install ('UNIX Development', 'System Tools', 'Command Line Tools', or 'Command Line Support').
- (Optional) The X11 windowing environment, for ports that depend on the functionality it provides to run. You have multiple choices for an X11 server:
- Install the xorg-server port from MacPorts (recommended).
- The XQuartz Project provides a complete X11 release for macOS including server and client libraries and applications.
- Apple's X11.app is provided by the “X11 User” package on older OS versions. It is always installed on Lion, and is an optional installation on your system CDs/DVD with previous OS versions.
macOS Package (.pkg) Installer
The easiest way to install MacPorts on a Mac is by downloading the pkg or dmg for Big Sur, Catalina, Mojave, High Sierra, Sierra, El Capitan, Yosemite, Mavericks, Mountain Lion, Lion, Snow Leopard, Leopard or Tiger and running the system's Installer by double-clicking on the pkg contained therein, following the on-screen instructions until completion.
This procedure will place a fully-functional and default MacPorts installation on your host system, ready for usage. If needed your shell configuration files will be adapted by the installer to include the necessary settings to run MacPorts and the programs it installs, but you may need to open a new shell for these changes to take effect.
The MacPorts “selfupdate” command will also be run for you by the installer to ensure you have our latest available release and the latest revisions to the “Portfiles” that contain the instructions employed in the building and installation of ports. After installation is done, it is recommended that you run this step manually on a regular basis to to keep your MacPorts system always current:
At this point you should be ready to enjoy MacPorts!
Type “man port” at the command line prompt and/or browse over to our Guide to find out more information about using MacPorts. Help is also available.
Source Installation
If on the other hand you decide to install MacPorts from source, there are still a couple of things you will need to do after downloading the tarball before you can start installing ports, namely compiling and installing MacPorts itself:
- “cd” into the directory where you downloaded the package and run “tar xjvf MacPorts-2.7.1.tar.bz2” or “tar xzvf MacPorts-2.7.1.tar.gz”, depending on whether you downloaded the bz2 tarball or the gz one, respectively.
- Build and install the recently unpacked sources:
- cd MacPorts-2.7.1
- ./configure && make && sudo make install
- cd ../
- rm -rf MacPorts-2.7.1*
These steps need to be perfomed from an administrator account, for which “sudo” will ask the password upon installation. This procedure will install a pristine MacPorts system and, if the optional steps are taken, remove the as of now unnecessary MacPorts-2.7.1 source directory and corresponding tarball.
To customize your installation you should read the output of “./configure --help | more” and pass the appropriate options for the settings you wish to tweak to the configuration script in the steps detailed above.
You will need to manually adapt your shell's environment to work with MacPorts and your chosen installation prefix (the value passed to configure's --prefix flag, defaulting to /opt/local):
- Add ${prefix}/bin and ${prefix}/sbin to the start of your PATH environment variable so that MacPorts-installed programs take precedence over system-provided programs of the same name.
- If a standard MANPATH environment variable already exists (that is, one that doesn't contain any empty components), add the ${prefix}/share/man path to it so that MacPorts-installed man pages are found by your shell.
- For Tiger and earlier only, add an appropriate X11 DISPLAY environment variable to run X11-dependent programs, as Leopard takes care of this requirement on its own.
Lastly, you need to synchronize your installation with the MacPorts rsync server:
Upon completion MacPorts will be ready to install ports!
It is recommended to run the above command on a regular basis to keep your installation current. Type “man port” at the command line prompt and/or browse over to our Guide to find out more information about using MacPorts. Help is also available.
Git Sources
If you are developer or a user with a taste for the bleeding edge and wish for the latest changes and feature additions, you may acquire the MacPorts sources through git. See the Guide section on installing from git.
Purpose-specific branches are also available at the https://github.com/macports/macports-base/branches url.
Alternatively, if you'd simply like to view the git repository without checking it out, you can do so via the GitHub web interface.
Selfupdate
Install Putty On Mac Catalina Os
If you already have MacPorts installed and have no restrictions to use the rsync networking protocol (tcp port 873 by default), the easiest way to upgrade to our latest available release, 2.7.1, is by using the selfupdate target of the port(1) command. This will both update your ports tree (by performing a sync operation) and rebuild your current installation if it's outdated, preserving your customizations, if any.
Other Platforms
Running on platforms other than macOS is not the main focus of The MacPorts Project, so remaining cross-platform is not an actively-pursued development goal. Nevertheless, it is not an actively-discouraged goal either and as a result some experimental support does exist for other POSIX-compliant platforms such as *BSD and GNU/Linux.
The full list of requirements to run MacPorts on these other platforms is as follows (we assume you have the basics such as GCC and X11):
- Tcl (8.4 or 8.5), with threads.
- mtree for directory hierarchy.
- rsync for syncing the ports.
- cURL for downloading distfiles.
- SQLite for the port registry.
- GNUstep (Base), for Foundation (optional, can be disabled via configure args).
- OpenSSL for signature verification, and optionally for checksums. libmd may be used instead for checksums.
Normally you must install from source or from an git checkout to run MacPorts on any of these platforms.
Install Putty On Mac Catalina Download
Help
Help on a wide variety of topics is also available in the project Guide and through our Trac portal should you run into any problems installing and/or using MacPorts. Of particular relevance are the installation & usage sections of the former and the FAQ section of the Wiki, where we keep track of questions frequently fielded on our mailing lists.
If any of these resources do not answer your questions or if you need any kind of extended support, there are many ways to contact us!
Comments are closed.