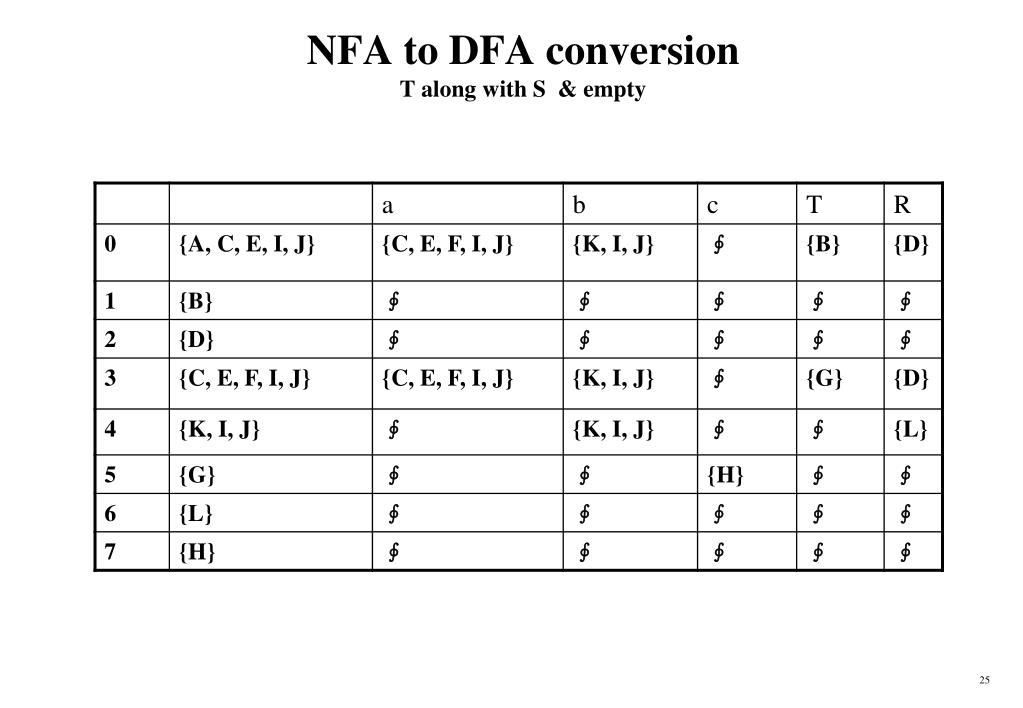
/* C program to implement Simple LR Parser. */
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int i,j,k,m,n=0,o,p,ns=0,tn=0,rr=0,ch=0;
char read[15][10],gl[15],gr[15][10],temp,templ[15],tempr[15][10],*ptr,temp2[5],dfa[15][15];
struct states
{
char lhs[15],rhs[15][10];
int n;
}I[15];
int compstruct(struct states s1,struct states s2)
{
int t;
if(s1.n!=s2.n)
return 0;
if( strcmp(s1.lhs,s2.lhs)!=0 )
return 0;
for(t=0;t<s1.n;t++)
if( strcmp(s1.rhs[t],s2.rhs[t])!=0 )
return 0;
return 1;
}
void moreprod()
{
int r,s,t,l1=0,rr1=0;
char *ptr1,read1[15][10];
for(r=0;r<I[ns].n;r++)
{
ptr1=strchr(I[ns].rhs[l1],'.');
t=ptr1-I[ns].rhs[l1];
if( t+1strlen(I[ns].rhs[l1]) )
{
l1++;
continue;
}
temp=I[ns].rhs[l1][t+1];
l1++;
for(s=0;s<rr1;s++)
if( tempread1[s][0] )
break;
if(srr1)
{
read1[rr1][0]=temp;
rr1++;
}
else
continue;
for(s=0;s<n;s++)
{
if(gl[s]temp)
{
I[ns].rhs[I[ns].n][0]='.';
I[ns].rhs[I[ns].n][1]=NULL;
strcat(I[ns].rhs[I[ns].n],gr[s]);
I[ns].lhs[I[ns].n]=gl[s];
I[ns].lhs[I[ns].n+1]=NULL;
I[ns].n++;
}
}
}
}
void canonical(int l)
{
int t1;
char read1[15][10],rr1=0,*ptr1;
for(i=0;i<I[l].n;i++)
{
temp2[0]='.';
ptr1=strchr(I[l].rhs[i],'.');
t1=ptr1-I[l].rhs[i];
if( t1+1strlen(I[l].rhs[i]) )
continue;
temp2[1]=I[l].rhs[i][t1+1];
temp2[2]=NULL;
for(j=0;j<rr1;j++)
if( strcmp(temp2,read1[j])0 )
break;
if(jrr1)
{
strcpy(read1[rr1],temp2);
read1[rr1][2]=NULL;
rr1++;
}
else
continue;
for(j=0;j<I[0].n;j++)
{
ptr=strstr(I[l].rhs[j],temp2);
if( ptr )
{
templ[tn]=I[l].lhs[j];
templ[tn+1]=NULL;
strcpy(tempr[tn],I[l].rhs[j]);
tn++;
}
}
for(j=0;j<tn;j++)
{
ptr=strchr(tempr[j],'.');
p=ptr-tempr[j];
tempr[j][p]=tempr[j][p+1];
tempr[j][p+1]='.';
I[ns].lhs[I[ns].n]=templ[j];
I[ns].lhs[I[ns].n+1]=NULL;
strcpy(I[ns].rhs[I[ns].n],tempr[j]);
I[ns].n++;
}
moreprod();
for(j=0;j<ns;j++)
{
//if ( memcmp(&I[ns],&I[j],sizeof(struct states))1 )
if( compstruct(I[ns],I[j])1 )
{
I[ns].lhs[0]=NULL;
for(k=0;k<I[ns].n;k++)
I[ns].rhs[k][0]=NULL;
I[ns].n=0;
dfa[l][j]=temp2[1];
break;
}
}
if(j<ns)
{
tn=0;
for(j=0;j<15;j++)
{
templ[j]=NULL;
tempr[j][0]=NULL;
}
continue;
}
dfa[l][j]=temp2[1];
printf('nnI%d :',ns);
for(j=0;j<I[ns].n;j++)
printf('nt%c -> %s',I[ns].lhs[j],I[ns].rhs[j]);
getch();
ns++;
tn=0;
for(j=0;j<15;j++)
{
templ[j]=NULL;
tempr[j][0]=NULL;
}
}
}
void main()
{
FILE *f;
int l;
clrscr();
for(i=0;i<15;i++)
{
I[i].n=0;
I[i].lhs[0]=NULL;
I[i].rhs[0][0]=NULL;
dfa[i][0]=NULL;
}
f=fopen('tab6.txt','r');
while(!feof(f))
{
fscanf(f,'%c',&gl[n]);
fscanf(f,'%sn',gr[n]);
n++;
}
printf('THE GRAMMAR IS AS FOLLOWSn');
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf('tttt%c -> %sn',gl[i],gr[i]);
I[0].lhs[0]='Z';
strcpy(I[0].rhs[0],'.S');
I[0].n++;
l=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
temp=I[0].rhs[l][1];
l++;
for(j=0;j<rr;j++)
if( tempread[j][0] )
break;
if(jrr)
{
read[rr][0]=temp;
rr++;
}
else
continue;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(gl[j]temp)
{
I[0].rhs[I[0].n][0]='.';
strcat(I[0].rhs[I[0].n],gr[j]);
I[0].lhs[I[0].n]=gl[j];
I[0].n++;
}
}
}
ns++;
printf('nI%d :n',ns-1);
for(i=0;i<I[0].n;i++)
printf('t%c -> %sn',I[0].lhs[i],I[0].rhs[i]);
for(l=0;l<ns;l++)
canonical(l);
printf('nnttPRESS ANY KEY FOR DFA TABLE');
getch();
clrscr();
printf('tttDFA TABLE IS AS FOLLOWSnnn');
for(i=0;i<ns;i++)
{
printf('I%d : ',i);
for(j=0;j<ns;j++)
if(dfa[i][j]!='0')
printf('%c'->I%d | ',dfa[i][j],j);
printf('nnn');
}
printf('nnnttPRESS ANY KEY TO EXIT');
getch();
}
Input File For SLR Parser:
S S+T
S T
T T*F
T F
F (S)
F t
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int i,j,k,m,n=0,o,p,ns=0,tn=0,rr=0,ch=0;
char read[15][10],gl[15],gr[15][10],temp,templ[15],tempr[15][10],*ptr,temp2[5],dfa[15][15];
struct states
{
char lhs[15],rhs[15][10];
int n;
}I[15];
int compstruct(struct states s1,struct states s2)
{
int t;
if(s1.n!=s2.n)
return 0;
if( strcmp(s1.lhs,s2.lhs)!=0 )
return 0;
for(t=0;t<s1.n;t++)
if( strcmp(s1.rhs[t],s2.rhs[t])!=0 )
return 0;
return 1;
}
void moreprod()
{
int r,s,t,l1=0,rr1=0;
char *ptr1,read1[15][10];
for(r=0;r<I[ns].n;r++)
{
ptr1=strchr(I[ns].rhs[l1],'.');
t=ptr1-I[ns].rhs[l1];
if( t+1strlen(I[ns].rhs[l1]) )
{
l1++;
continue;
}
temp=I[ns].rhs[l1][t+1];
l1++;
for(s=0;s<rr1;s++)
if( tempread1[s][0] )
break;
if(srr1)
{
read1[rr1][0]=temp;
rr1++;
}
else
continue;
for(s=0;s<n;s++)
{
if(gl[s]temp)
{
I[ns].rhs[I[ns].n][0]='.';
I[ns].rhs[I[ns].n][1]=NULL;
strcat(I[ns].rhs[I[ns].n],gr[s]);
I[ns].lhs[I[ns].n]=gl[s];
I[ns].lhs[I[ns].n+1]=NULL;
I[ns].n++;
}
}
}
}
void canonical(int l)
{
int t1;
char read1[15][10],rr1=0,*ptr1;
for(i=0;i<I[l].n;i++)
{
temp2[0]='.';
ptr1=strchr(I[l].rhs[i],'.');
t1=ptr1-I[l].rhs[i];
if( t1+1strlen(I[l].rhs[i]) )
continue;
temp2[1]=I[l].rhs[i][t1+1];
temp2[2]=NULL;
for(j=0;j<rr1;j++)
if( strcmp(temp2,read1[j])0 )
break;
if(jrr1)
{
strcpy(read1[rr1],temp2);
read1[rr1][2]=NULL;
rr1++;
}
else
continue;
for(j=0;j<I[0].n;j++)
{
ptr=strstr(I[l].rhs[j],temp2);
if( ptr )
{
templ[tn]=I[l].lhs[j];
templ[tn+1]=NULL;
strcpy(tempr[tn],I[l].rhs[j]);
tn++;
}
}
for(j=0;j<tn;j++)
{
ptr=strchr(tempr[j],'.');
p=ptr-tempr[j];
tempr[j][p]=tempr[j][p+1];
tempr[j][p+1]='.';
I[ns].lhs[I[ns].n]=templ[j];
I[ns].lhs[I[ns].n+1]=NULL;
strcpy(I[ns].rhs[I[ns].n],tempr[j]);
I[ns].n++;
}
moreprod();
for(j=0;j<ns;j++)
{
//if ( memcmp(&I[ns],&I[j],sizeof(struct states))1 )
if( compstruct(I[ns],I[j])1 )
{
I[ns].lhs[0]=NULL;
for(k=0;k<I[ns].n;k++)
I[ns].rhs[k][0]=NULL;
I[ns].n=0;
dfa[l][j]=temp2[1];
break;
}
}
if(j<ns)
{
tn=0;
for(j=0;j<15;j++)
{
templ[j]=NULL;
tempr[j][0]=NULL;
}
continue;
}
dfa[l][j]=temp2[1];
printf('nnI%d :',ns);
for(j=0;j<I[ns].n;j++)
printf('nt%c -> %s',I[ns].lhs[j],I[ns].rhs[j]);
getch();
ns++;
tn=0;
for(j=0;j<15;j++)
{
templ[j]=NULL;
tempr[j][0]=NULL;
}
}
}
void main()
{
FILE *f;
int l;
clrscr();
for(i=0;i<15;i++)
{
I[i].n=0;
I[i].lhs[0]=NULL;
I[i].rhs[0][0]=NULL;
dfa[i][0]=NULL;
}
f=fopen('tab6.txt','r');
while(!feof(f))
{
fscanf(f,'%c',&gl[n]);
fscanf(f,'%sn',gr[n]);
n++;
}
printf('THE GRAMMAR IS AS FOLLOWSn');
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf('tttt%c -> %sn',gl[i],gr[i]);
I[0].lhs[0]='Z';
strcpy(I[0].rhs[0],'.S');
I[0].n++;
l=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
temp=I[0].rhs[l][1];
l++;
for(j=0;j<rr;j++)
if( tempread[j][0] )
break;
if(jrr)
{
read[rr][0]=temp;
rr++;
}
else
continue;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(gl[j]temp)
{
I[0].rhs[I[0].n][0]='.';
strcat(I[0].rhs[I[0].n],gr[j]);
I[0].lhs[I[0].n]=gl[j];
I[0].n++;
}
}
}
ns++;
printf('nI%d :n',ns-1);
for(i=0;i<I[0].n;i++)
printf('t%c -> %sn',I[0].lhs[i],I[0].rhs[i]);
for(l=0;l<ns;l++)
canonical(l);
printf('nnttPRESS ANY KEY FOR DFA TABLE');
getch();
clrscr();
printf('tttDFA TABLE IS AS FOLLOWSnnn');
for(i=0;i<ns;i++)
{
printf('I%d : ',i);
for(j=0;j<ns;j++)
if(dfa[i][j]!='0')
printf('%c'->I%d | ',dfa[i][j],j);
printf('nnn');
}
printf('nnnttPRESS ANY KEY TO EXIT');
getch();
}
Input File For SLR Parser:
S S+T
S T
T T*F
T F
F (S)
F t

LOGIC:
Building SLR Parse Tables The easiest technique for generating LR-based parse table is known as SLR (Simple LR). Understanding this technique should provide you with what you need to know to understand how LR parsers work in general; it is also the foundation for the more complex techniques (LR and LALR).
Read the input string.
- Several implementations in Python language of some of the parsing techniques such as LL(1) parsing, SLR(1) parsing,LR(0) parsing and LR(1) parsing. Programming-language parser parsing compiler lr-parser grammar python3 ll-parser context-free-grammar compiler-design compiler-construction ll-grammar slr-parser first-follow-compiler first-follow.
- ←Business Intelligence Multiple Choice Questions. C Program to check number is palindrome →. Implementation of SLR Parser.
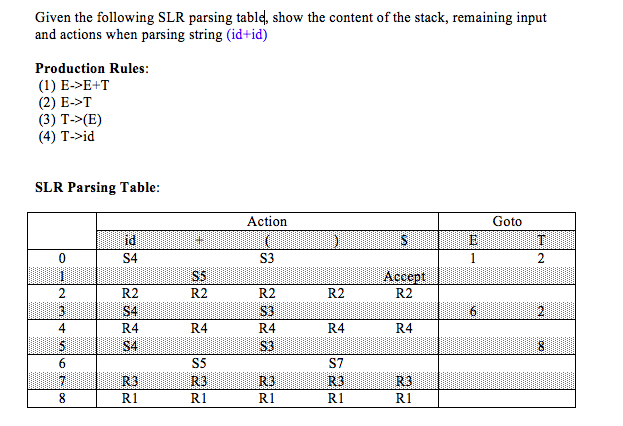
Using predictive parsing table parse the given input using stack .
If stack [i] matches with token input string pop the token else shift it repeat the process until it reaches to $.
C Programming String Parsing
RESOURCE:
Turbo C++
| INPUT & OUTPUT: | |
| Enter the input string:i*i+i | |
| Stack | INPUT |
| $bt | i*i+i$ |
| $bcf | i*i+i$ |
| $bci | i*i+i$ |
| $bc | *i+i$ |
| $bcf* | *i+i$ |
| $bcf | i+i$ |
| $bci | i+i$ |
| $bc | +i$ |
| $b | +i$ |
| $bt+ | +i$ |
| $bt | i$ |
| $bcf | i$ |
| $ bci | i$ |
| $bc | $ |
| $b | $ |
| $ | $ |
| success |
C program for implementing the functionalities of predictive parser
Slr Parsing Table Program In California
C program to Construct of recursive descent parsing for the following grammar E->TE’ E’->+TE/@ T->FT’ T`->*FT’/@ F->(E)/ID where”@ represents null character”
Comments are closed.